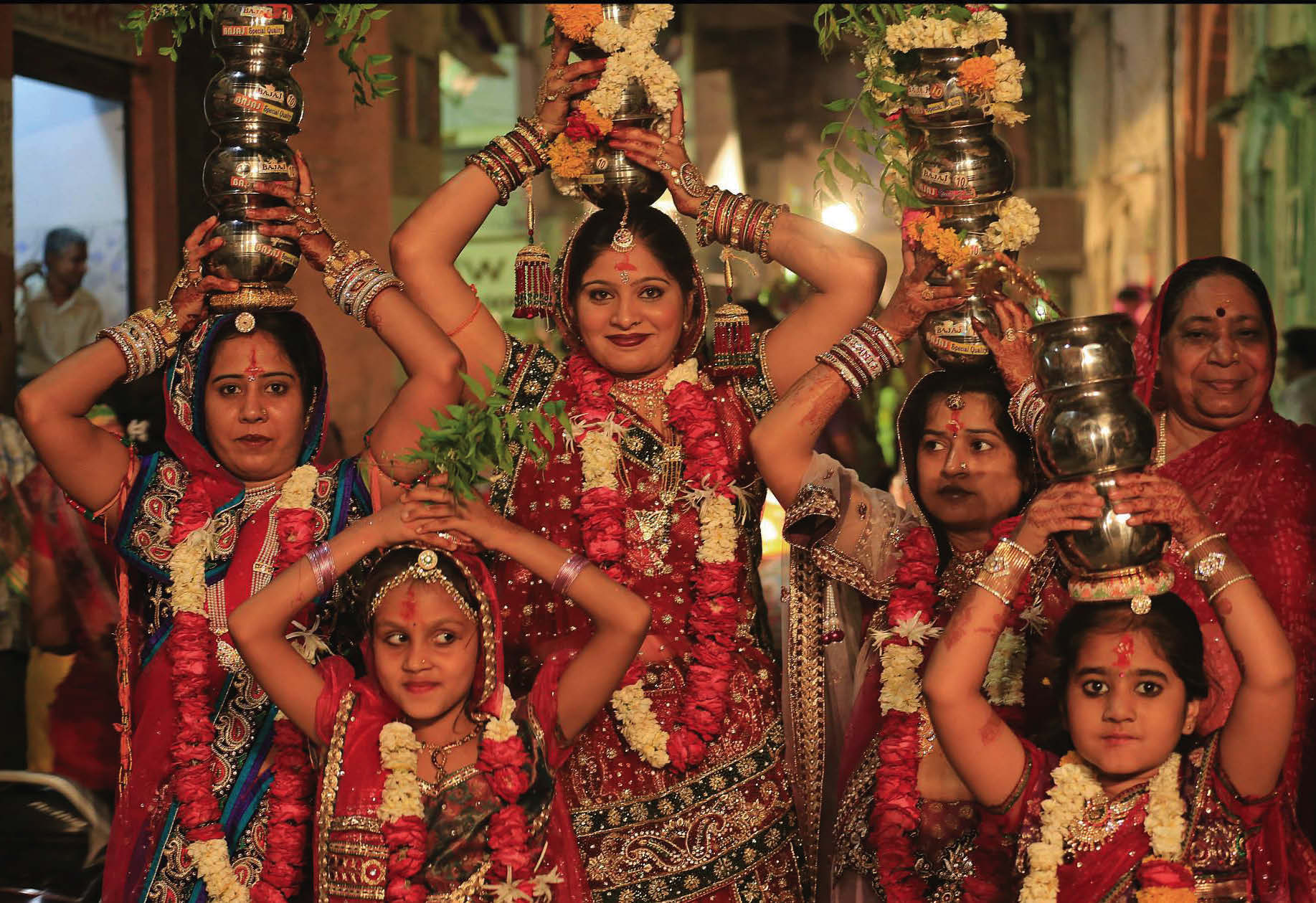
Gangaur is a festival celebrated in the Indian state of Rajasthan and some parts of Gujarat, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh.
Gangaur is colourful and one of the most important festivals of people of Rajasthan and is observed throughout the state with great fervour and devotion by womenfolk who worship Gauri, the consort of Lord Shiva during March–April. It is the celebration of spring, harvest and marital fidelity. Gana is a synonym for Lord Shiva and Gaur which stands for Gauri or Parvati who symbolizes Saubhagya (marital bliss). The unmarried women worship her for being blessed with a good husband, while married women do so for the welfare, health and long life of their husbands and for a happy married life. People from Rajasthan when migrated to Kolkata in West Bengal started celebrating Gangaur. This celebration is now more than 100 years old in Kolkata.
Rites and Rituals
The festival commences on the first day of chaitra, the day following Holi and continues for 16 days. For a newly-wedded girl, it is binding to observe the full course of 18 days of the festival that succeeds her marriage. Even unmarried girls fast for the full period of the 18 days and eat only one meal a day. Festivity consummates on 3rd day of Shukla Paksha of Chaitra Month.Fairs (Gangaur Melas) are held throughout the 18 day period. Numerous folklores are associated with Gangaur which makes this festival deeply ingrained into the hearts of Rajasthan, and parts of Madhya Pradesh, Haryana & Gujarat.
Images and Paintings
Images of Isar and [Parvati |Gauri]are made of clay for the festival. In some Rajput families, permanent wooden images are painted afresh every year by reputed painters called matherans on the eve of festival. A distinct difference between the idols of Teej and Gangaur is that the Idol will have a canopy during the Teej Festival while the Gangaur idol would not have a canopy.
Mehandi
The ladies decorate their hands and feet by drawing designs with Mehndi (myrtle paste). The figures drawn range from the Sun, Moon and the starts to simple flowers or geometrical designs. Ghudlias are earthen pots with numerous holes all around and a lamp lit inside them. On the evening of the 7th day after Holi, unmarried girls go around singing songs of ghudlia carrying the pots with a burning lamp inside, on their heads. On their way, they collect small presents of cash, sweets, jaggery, ghee, oil etc. this continues for 10 days i.e. up to the conclusion of the Gangaur festival when the girls break their pots and throw the debris into the well or a tank and enjoys a feast with the collection made.
Gauri’s Departure
The festival reaches its climax during the last three days. The images of Gauri and Isar are dressed in new garments especially made for the occasion. Unmarried girls and married women decorate the images and make them look like living figures.
At an auspicious hour in the afternoon, a procession is taken out to a garden, bawdi or johad or well with the images of Isar and Gauri, placed on the heads of married women. Songs are sung about the departure of Gauri to her husband’s house. The procession comes back after offering water to the first two days. On the final day, she faces in the same direction as Isar and the procession concludes in the consignment of the all images in the waters of a tank or a well. The women bid farewell to Gauri and turn their eyes and the Gangaur festival comes to an end.
The festival celebrates the union of Shiva and Parvati which gives young girls and boys an occasion to interact with each other. It is an elaborate occasion and there are several rituals associated with it.
These rituals include:
- Collecting ash from Holika Dehan and burying seeds of wheat and barley in it and protecting them by watering till the seeds germinate.
- Songs in praise of Shiv and Parvati are sung by women who also carry pots on their heads.
- Women make clay images of both Shiva and Parvati.
- A procession is taken by young girls and all of them place an earthern pot with holes and lamp inside on their heads. They distribute cash and other gifts on their way.
- The final day of the festival sees images of Gauri being taken out in a procession accompanied by camels, bullock carts, horses and elephants. The procession is symbolic of return of Gauri to her husband’s (Shiv’s) home.
- To mark the end of the procession, the girls break their pots.
- Apart from these rituals, newly married women fast for the whole eighteen days of the festival and even unmarried women fast and eat only one meal a day in the hope to find a good husband. During this festival in Jaipur, a popular sweet dish called ‘Ghewar’ is distributed between families, relatives and friends.





Be the first to comment